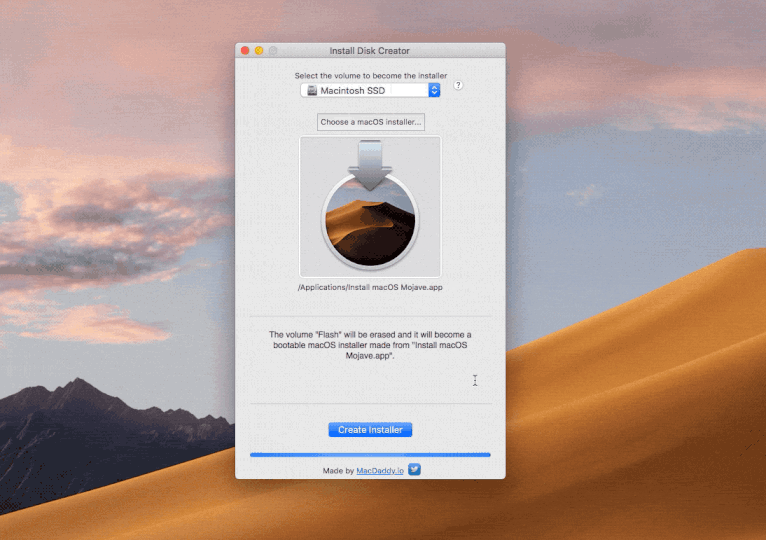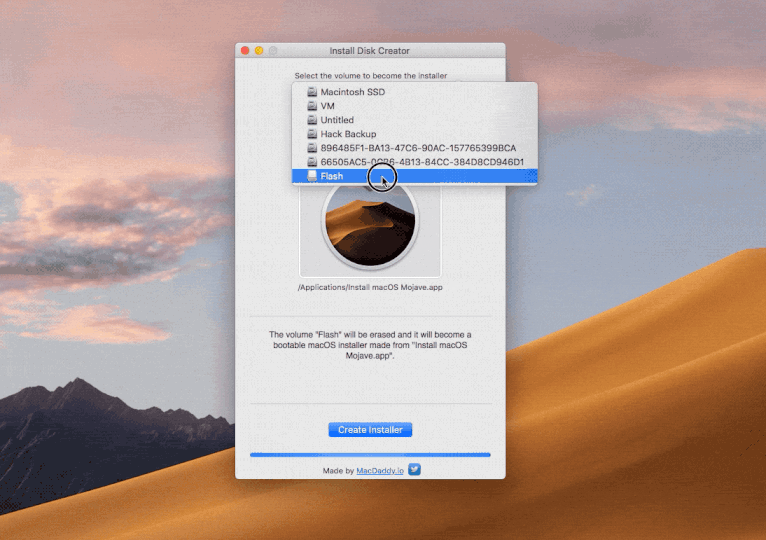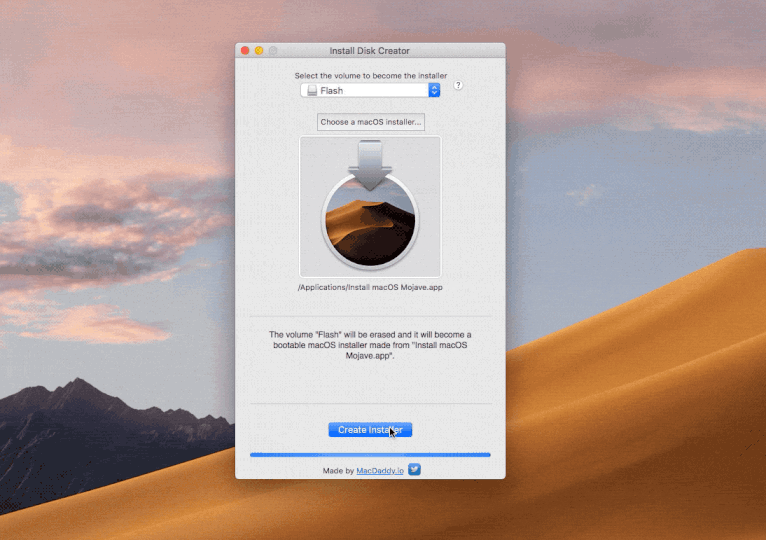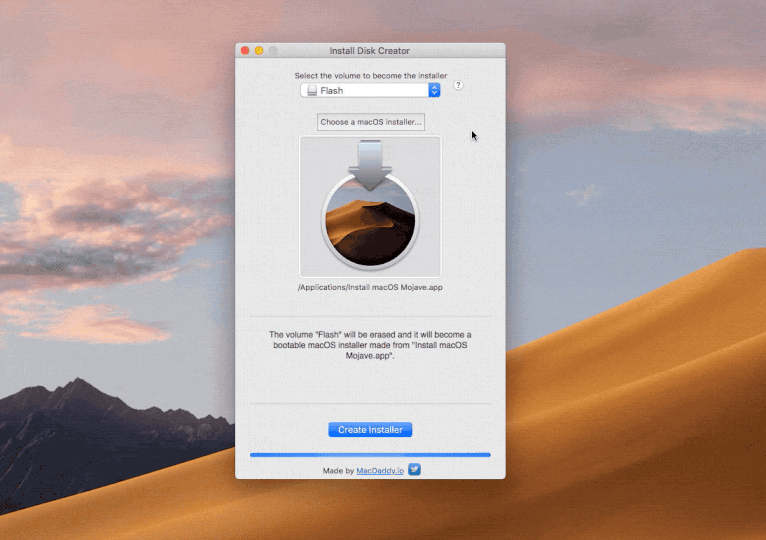
Windows Version. Select the recovery disk. To recover data from a Mac hard disk, please select the hard drive where you want to restore Mac data. Click the 'Start' button to move forward. Scan the Mac recovery disk. Recoverit Mac Disk Recovery will start an instant and all-around scan on the recovery disk. If you bought a new machine from Apple you have OS X 10.8 already installed – but no back up disk! To create a bootable Mac drive you need any disk with Mac OS X 10.8.5 or newer (10.9, 10.10, 10.11 El Capitan, 10.12 Sierra, 10.13 High Sierra, and 10.14 Mojave included) either running as your main system, or just being installed on a drive that's connected to your Mac at the moment. Starting Disk Utility on a Mac. Click on the Spotlight icon on the top right of the menu bar. Type in “disk utility”. Hit Enter to open Disk Utilities. Open a Finder window. Click on Applications in the left window. Scroll down and click on the Utilities folder. An alert appears that says, “A software update is required to use this startup disk”. Click the Update button. You will need an internet connection (click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar.
On every OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion there is a hidden partition to enable a method for Mountain Lion OS to be reinstalled on the machine, it is known as the Recovery Partition or drive and is 650mb in size.
If you bought a new machine from Apple you have OS X 10.8 already installed – but no back up disk! and since you haven’t bought the OSX Lion 10.8 App from the App store you can’t re-download it – so thats why you have the recovery drive as a partition in your main hard drive, to boot from it you need to restart the machine and when it starts to boot hold down “command” + “r” keys.
To create a bootable Mac drive you need any disk with Mac OS X 10.8.5 or newer (10.9, 10.10, 10.11 El Capitan, 10.12 Sierra, 10.13 High Sierra, and 10.14 Mojave included) either running as your main system, or just being installed on a drive that's connected to your Mac at the moment. Jun 12, 2020 The version of macOS offered by macOS Recovery might vary in some cases: If macOS Sierra 10.12.4 or later has never been installed on this Mac, Option-Command-R installs the macOS that came with your Mac, or the closest version still available. And Shift-Option-Command-R isn't available. If you erased your entire disk instead of just the startup volume on that disk, macOS Recovery might.
From the Recovery Partition Hard Drivr you can run Disk Utility, access the command line, get online help and do a restore from a Time Machine backup and re-install Mountain Lion leaving all your other files intact – it just replaces the core operating system.
You can make a bootable USB drive or disk from the Recovery Partition 2 ways – the easy way and on the Terminal
The Easy Way
1) Download OSX Recovery Disk Assistant and uncompress and launch it
2) Attach the USB drive that you want to copy the Recovery Partition to.
3) Select the drive and continue (All contents on it will be erased)
That’s it one external bootable Recovery Drive – this works on both OSX 10.7 and 10.8
Create A Hd Drive Image Using Mac Os X 10.88 Download Free
The Terminal Way
1) Launch Terminal from /Applications/Utilities and run:
The main drive in this list is No.2 with the “Identifier” of disk0s2, the boot Recovery HD drive is disk0s3
Mac os x flash drive encryption. We can also identify the Recovery drive by the name and the size – set at 650mb
2) Mount the drive by its Identifier:
Output should be:
Now the Recovery HD is mounted in the Finder and you can see it in the sidebar under Devices
Navigate to it from the sidebar – Recovery HD/com.apple.recovery.boot/BaseSystem.dmg
recovery-finder-osx-lion
3) Doubleclick BaseSystem.dmg to mount it also in the sidebar. This will mount the volume ” Mac OSX Base System”
macosx-basesystem
4) Open Disk Utility in /Applications/Utilities
5) Put in a 2GB+ USB drive, let Disk Utility load it. The USB drive needs to be formatted as Mac OS Extended Journaled, if its not, its time to format it in Disk Utility…
6) Finally in still in Disk Utility, select the “Restore” tab – drag the mounted volume “Mac OSX Base System” into the Source field and drag the USB drive “Volume” (mine is called SuperBootUSBDrive) to the Destination.
restore-volume-osx-usb
7) Click Restore – 10 minutes later – One bootable USB drive
Your bootable USB drive will be called “Mac OS X Base System” after the restore is complete. Now to boot from it just select it as the Start Up disk in System Preferences or hold down option key on boot and select it from the choice of bootable devices. Mac os x mount usb drive single user mode.
If you have downloaded the OSX 10.8 Mountain Lion App from the App Store then you can also make a full bootable image of OSX 10.8 to a disk/drive, you need to make the boot drive/disk before you install the Mountain Lion App, as the installer is deleted after running it. That’s why the guide here can get you out of trouble.
Update For Newer Models – hidden BaseSystem.dmg – BaseSystem.chunklist
If you have the latest models from Apple that came already shipped with OSX 10.7, then you may not have the “BaseSystem.dmg” but instead see a “BaseSystem.chunklist” , the “BaseSystem.dmg” is there it’s just hidden.
To show it so you can see it in the finder – go to Terminal – and after you have mounted the Recovery Drive:
Now it will be visible in the Finder.
Erasing your disk: For most reasons to erase, including when reformatting a disk or selling, giving away, or trading in your Mac, you should erase your entire disk.
Erasing a volume on your disk: In other cases, such as when your disk contains multiple volumes (or partitions) and you don't want to erase them all, you can erase specific volumes on the disk.
Erasing a disk or volume permanently deletes all of its files. Before continuing, make sure that you have a backup of any files that you want to keep.
How to erase your disk
- Start up from macOS Recovery. Then select Disk Utility from the Utilities window and click Continue.
If you're not erasing the disk your Mac started up from, you don't need to start up from macOS Recovery: just open Disk Utility from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. - Choose View > Show All Devices from the menu bar in Disk Utility. The sidebar now shows your disks (devices) and any containers and volumes within them. The disk your Mac started up from is at the top of the list. In this example, Apple SSD is the startup disk:
- Select the disk that you want to erase. Don't see your disk?
- Click Erase, then complete these items:
- Name: Type the name that you want the disk to have after you erase it.
- Format: Choose APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Disk Utility shows a compatible format by default.
- Scheme: Choose GUID Partition Map.
- Click Erase to begin erasing your disk and every container and volume within it. You might be asked to enter your Apple ID. Forgot your Apple ID?
- When done, quit Disk Utility.
- If you want your Mac to be able to start up from the disk you erased, reinstall macOS on the disk.
How Do I Download A Dvd Onto My Mac
How to erase a volume on your disk
- Start up from macOS Recovery. Then select Disk Utility from the Utilities window and click Continue.
If you're not erasing the volume your Mac started up from, you don't need to start up from macOS Recovery: just open Disk Utility from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. - In the sidebar of Disk Utility, select the volume that you want to erase. The volume your Mac started up from is named Macintosh HD, unless you changed its name. Don't see your volume?
- Click Erase, then complete these items:
- Name: Type the name that you want the volume to have after you erase it.
- Format: Choose APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Disk Utility shows a compatible format by default.
- If you see an Erase Volume Group button, the volume you selected is part of a volume group. In that case, you should erase the volume group. Otherwise, click Erase to erase just the selected volume. You might be asked to enter your Apple ID. Forgot your Apple ID?
- When done, quit Disk Utility.
- If you want your Mac to be able to start up from the volume you erased, reinstall macOS on that volume.
Reasons to erase
You can erase at any time, including in circumstances such as these:
- You want to permanently erase all content from your Mac and restore it to factory settings. This is one of the final steps before selling, giving away, or trading in your Mac.
- You're changing the format of a disk, such as from a PC format (FAT, ExFAT, or NTFS) to a Mac format (APFS or Mac OS Extended).
- You received a message that your disk isn't readable by this computer.
- You're trying to resolve a disk issue that Disk Utility can't repair.
- The macOS installer doesn't see your disk or can't install on it. For example, the installer might say that your disk isn't formatted correctly, isn't using a GUID partition scheme, contains a newer version of the operating system, or can't be used to start up your computer.
- The macOS installer says that you may not install to this volume because it is part of an Apple RAID.
About APFS and Mac OS Extended
Disk Utility in macOS High Sierra or later can erase using either the newer APFS (Apple File System) format or the older Mac OS Extended format, and it automatically chooses a compatible format for you.
How to choose between APFS and Mac OS Extended

Disk Utility tries to detect the type of storage and show the appropriate format in the Format menu. If it can't, it chooses Mac OS Extended, which works with all versions of macOS. If you want to change the format, answer these questions:
- Are you formatting the disk that came built into your Mac?
If the built-in disk came APFS-formatted, Disk Utility suggests APFS. Don't change it to Mac OS Extended. - Are you about to install macOS High Sierra or later for the first time on the disk?
If you need to erase your disk before installing High Sierra or later for the first time on that disk, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled). During installation, the macOS installer decides whether to automatically convert to APFS—without erasing your files. - Are you preparing a Time Machine backup disk or bootable installer?
Choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled) for any disk that you plan to use as a Time Machine backup disk or as a bootable installer. - Will you be using the disk with another Mac?
If the other Mac isn't using macOS High Sierra or later, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Earlier versions of macOS don't work with APFS-formatted volumes.
How to identify the format currently in use
If you want to know which format is currently in use, use any of these methods:
Create A Hd Drive Image Using Mac Os X 10.88 5

- Select the volume in the Disk Utility sidebar, then check the information shown on the right. For more detail, choose File > Get Info from the Disk Utility menu bar.
- Open System Information and select Storage in the sidebar. The File System column on the right shows the format of each volume.
- Select the volume in the Finder, then choose File > Get Info from the menu bar. The Get Info window shows the Format of that volume.
If your disk or volume doesn't appear, or the erase fails
- Shut down your Mac, then unplug all nonessential devices from your Mac.
- If you're erasing an external drive, make sure that it's connected directly to your Mac using a cable that you know is good. Then turn the drive off and back on.
- If your disk or volume still doesn't appear in Disk Utility, or Disk Utility reports that the erase process failed, your disk or Mac might need service. If you need help, please contact Apple Support.
Learn more
Create A Hd Drive Image Using Mac Os X 10.88 Mountain Lion
How To Download A Disk On A Mac Desktop

How To Use Disk Drive
- If you can't start up from macOS Recovery, you can use a different startup disk instead.
- If Disk Utility shows a Security Options button in the Erase window, you can click that button to choose between a faster (but less secure) erase and a slower (but more secure) erase. Some older versions of Disk Utility offer the option to zero all data instead. These secure-erase options aren't offered or needed for solid-state drives (SSDs) and flash storage.